In the world of electromagnetics, permanent magnets have become an important object of research and application due to their persistent magnetic properties. The question of whether the magnetic poles of permanent magnets can be changed has always been a concern. To answer this question, we need to delve into the magnetic sources of permanent magnets, the nature of magnetic poles, and related physical principles.
The magnetism of permanent magnets originates from the microstructure of their internal atoms. Inside a permanent magnet, there are a large number of magnetic domains, which are small regions formed by the orderly arrangement of many magnetic atoms. In the natural state, the arrangement direction of these magnetic domains is disordered, and their magnetism cancels each other out, making the entire object not exhibit magnetism. And when an object is magnetized, under the action of an external magnetic field, the magnetic domains will be arranged neatly along the direction of the magnetic field, thus making the object exhibit magnetism as a whole, forming two magnetic poles, the South Pole and the North Pole.
In theory, the magnetic poles of permanent magnets can be changed, but this requires specific conditions and methods. The most common method is to achieve magnetic pole reversal by strengthening the magnetic field externally. When a sufficiently strong reverse magnetic field is applied to a permanent magnet, as the magnetic field strength gradually increases, the originally neatly arranged magnetic domains will be subjected to a reverse force. When the strength of the reverse magnetic field exceeds the coercive force of the permanent magnet, the arrangement direction of the magnetic domains will reverse, resulting in a change in the magnetic pole of the permanent magnet. However, this method requires a high level of magnetic field strength, and different types of permanent magnets have varying coercivity, resulting in differences in the required reverse magnetic field strength. For example, some permanent magnets with high coercivity require a very strong reverse magnetic field to achieve pole reversal.
In addition to strengthening the magnetic field, high temperatures may also have an impact on the magnetic poles of permanent magnets. Each type of permanent magnet has its specific Curie temperature. When a permanent magnet is heated above the Curie temperature, the arrangement of its internal magnetic domains becomes disordered, and the magnetism almost completely disappears. At this point, the magnetic poles no longer exist. If a reverse magnetic field is applied during the cooling process, when the temperature drops below the Curie temperature, the magnetic domains will rearrange under the action of the reverse magnetic field, forming new magnetic poles and achieving a change in magnetic poles. However, it should be noted that high temperatures may cause damage to the structure of permanent magnets, affecting their magnetic properties and even preventing them from restoring their original magnetism. Therefore, this method requires careful control of temperature and cooling process when applied.
However, not all permanent magnets can easily change their magnetic poles. Some permanent magnets have high coercivity due to their material properties, and changing their magnetic poles requires very harsh conditions, which are difficult to achieve in practical applications. Moreover, even if the magnetic pole of a permanent magnet can be changed, multiple pole reversals may have adverse effects on its magnetic properties, leading to weakened or unstable magnetism.
In practical applications, changing the magnetic poles of permanent magnets is relatively rare. The reason why permanent magnets are widely used is precisely because of their magnetic stability and durability. In most cases, people prefer permanent magnets to maintain stable magnetic poles and magnetism to meet the normal operational needs of various equipment and devices. For example, in equipment such as motors, generators, speakers, etc., the stability of the magnetic poles of permanent magnets is the key to ensuring equipment performance.
In summary, the magnetic poles of permanent magnets can be changed under specific conditions, and the reversal of magnetic poles can be achieved by strengthening the reverse magnetic field externally or combining high temperature with the reverse magnetic field. However, this process is influenced by various factors such as the characteristics of the permanent magnet material, magnetic field strength, temperature, etc., and requires careful operation in practical applications to avoid damaging the performance of the permanent magnet. In most cases, we focus more on the stability of permanent magnet poles to fully utilize their application value in various fields.
Can the magnetic poles of permanent magnets be changed
Time:2025/07/22
News
-
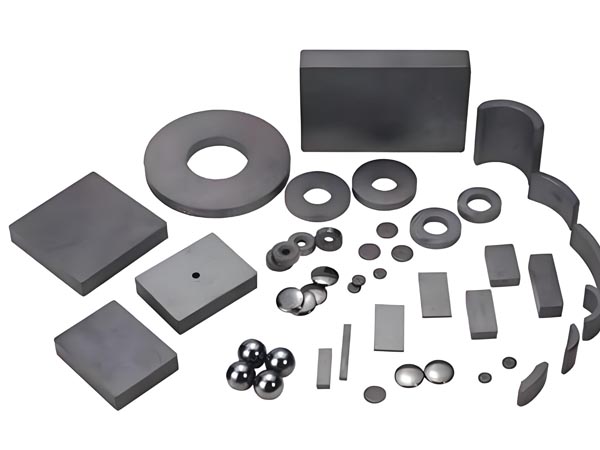

What are the types of shapes of strong neodymium iron boron magnets
Neodymium iron boron magnets, as the most powerful permanent magnet materials currently available, are known as the "magnetic king" and have a wide range of applications. In order to meet the needs of different scenarios, neodymium iron boron magnets are ... More >2025
07-22
-

Can the magnetic poles of permanent magnets be changed
In the world of electromagnetics, permanent magnets have become an important object of research and application due to their persistent magnetic properties. The question of whether the magnetic poles of permanent magnets can be changed has always been a c... More >2025
07-22